News Center
-
 Air Conditioning maintenance debugging must master the basic knowledge, these you understand? Oh, Shit 2020-04-10
Air Conditioning maintenance debugging must master the basic knowledge, these you understand? Oh, Shit 2020-04-10Air Conditioning maintenance debugging must master the basic knowledge, these you understand? Oh, Shit
here are many methods of refrigeration, commonly used are: gas expansion refrigeration, liquid gasification refrigeration, vortex tube refrigeration and thermoelectric refrigeration. Liquid gasification refrigeration is the most widely used, its working principle is the use of liquid gasification endothermic to achieve refrigeration. 1. Working principle of air conditioning (mainly refrigeration, heating the opposite) : The high temperature and high pressure refrigerant discharged from the compressor flows through the four-way valve ——— The refrigerant is transformed from a gas state to a liquid state, through a capillary (or solenoid) throttling and pressure-reducing single-way valve (outdoor high pressure pipe) , the refrigerant enters a chamber heat exchanger (realizing refrigeration) . Complete a single-loop refrigeration cycle.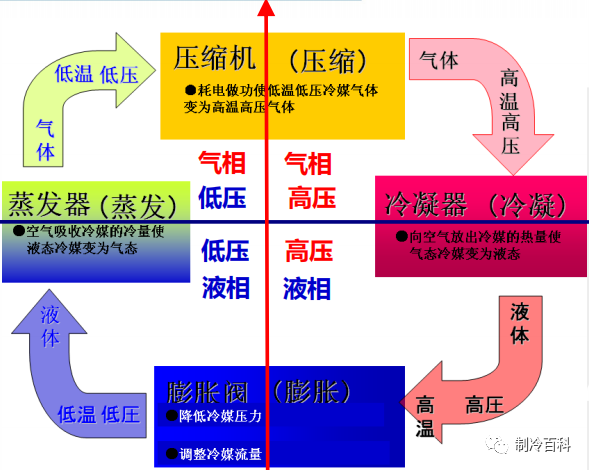
2, refrigeration system components: air conditioning refrigeration system is mainly composed of four major components and some auxiliary equipment in the refrigeration system. Four major parts are: compressor condenser throttling mechanism evaporator composition. Auxiliary Equipment: Oil Separator; drying filter; liquid storage tank; electromagnetic four-way Reversing Valve; solenoid valve; one-way Valve. 3. The working principle of each component compressor: as the "heart" of refrigeration system, it has important influence on the running performance, noise, energy consumption, vibration and service life of air conditioning. According to the thermodynamic principle, it can be divided into volume type and velocity type.
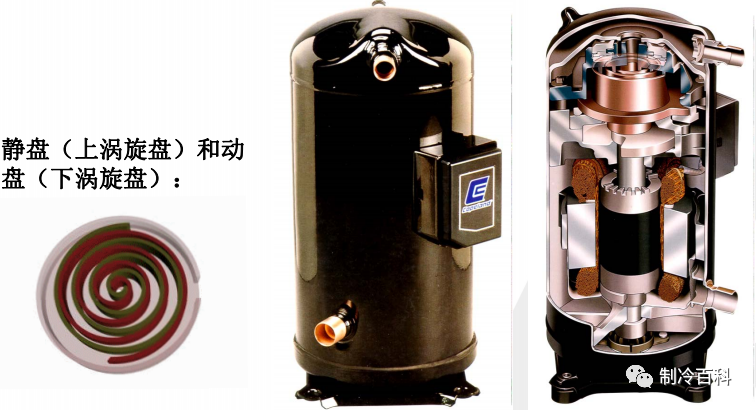

Volumetric type: A certain volume of gas inhaled into the cylinder and change the volume of the cylinder to achieve gas compression and forced discharge. Velocity type: The inhalation of gas to a certain speed, and then slow down, so that the kinetic energy into pressure and then out. The growth of the gas is due to the transformation of velocity. Scroll compressor: by The stator and Rotor two scroll body meshing from. Rotary compressor: by the eccentric wheel spindle, cylinder, sleeve, intake, skateboard, spring, exhaust valve, exhaust port composition. Condenser: the condenser is the refrigeration of the evaporator in the refrigeration system together with the power consumption of the compressor to the environment medium (cooling water or air) . According to cooling can be divided into air-cooled, water-cooled and evaporative. Cooling is mainly to the outdoor heat emission, heating to the outdoor absorption of heat. EVAPORATOR: The main function of the evaporator is to enter the throttle into the low-temperature and low-pressure refrigerant liquid boiling evaporation in the evaporator, absorbing the heat of the cooling medium, and then itself into a low-pressure saturated (usually some overheating) steam, it's being sucked away by the compressor. In other words, an evaporator is a heat exchanger that absorbs heat (i. e. outputs cold) . Throttling element: The throttling element is one of the four major components in the refrigeration system. Its main functions are: throttling and depressurizing the high-pressure liquid refrigerant, ensuring the pressure difference between the condenser and the evaporator, the refrigerant entering the evaporator is made to absorb heat and evaporate at low pressure under the requirement, thus achieving the aim of cooling down. Regulate the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator, so as to adapt to the load changes in the evaporator, so that the normal operation of the system.

CAPILLARY: a very thin tube, usually 0.5 ~ 2.5 mm in diameter and 1 ~ 5 M in length. When the refrigerant in the tube flow, the need to overcome the resistance in the tube, the natural generation of a certain pressure drop. Capillary features: Because in the normal state, when the compressor shutdown, high and low pressure can quickly balance, conducive to the compressor start again. The utility model has the advantages of simple structure, convenient manufacture and low price. For Heat pump systems, the refrigerant throttling process in the capillary tube, source: Refrigeration Encyclopedia Public, there is no import and export issues. In a capillary refrigeration system, the performance of the unit is very sensitive to the refrigerant charge. When the operating condition of the refrigeration system changes, the capillaries'ability to adjust the flow rate of refrigerant is poor. Because capillary inside diameter is small, conduit is long, be blocked easily, should notice system does not have inside dry with clean. Generally in front of the capillary tube set dry filter, in order to prevent blocking. Thermal Expansion Valve: the Control Valve that controls the amount of liquid supplied to the evaporator and is also the throttle valve of the refrigeration unit. Thermal expansion valve is the use of evaporator outlet refrigerant superheat changes to regulate the flow. According to the different structure can be divided into: Internal Balance and external balance. THERMAL EXPANSION VALVE DISADVANTAGES: Low Control Accuracy, Limited Adjustment Range, the valve body diaphragm deformation is limited, so that the change range of needle opening is small, so the flow of the adjustment range is small. Can Not be met when large flow regulation is required. The high temperature gas at the evaporator must first heat the shell of the temperature sensor, the shell of the temperature sensor has a large thermal inertia, resulting in the reaction lag electronic expansion valve: The application of the electronic expansion valve overcomes the shortcomings of the thermal expansion valve, it also provides the condition for the intellectualization of the refrigeration device. The electric signal produced by adjusting parameters is used to control the voltage or current applied to the expansion valve, so as to reach the goal of regulation. ELECTRONIC EXPANSION VALVE CLASSIFICATION: Electromagnetic Electronic Expansion Valve; electric electronic expansion valve. 4, Refrigeration System Auxiliary Equipment Oil separator: WORKING PRINCIPLE: compressor out of the high-pressure gas (gas and lubricating oil) , into the oil separator, into the oil separator will be separated from the working gas, down the inner wall of the cylinder. The working gas is drawn from the oil separator by a central tube through a perforated baffle. The separated oil, concentrated in the lower part of the oil separator, can be regularly discharged, or the use of floating ball valve, so that the oil automatically back to the compressor in the crankcase. DRYING FILTER: the role of the drying filter is to absorb water in the refrigeration system, blocking impurities in the system so that it can not pass, to prevent the refrigeration system pipeline ice block and dirty block. Since the most easily clogged part of the system is the CAPILLARY (or expansion valve) , the drying filter is usually installed between the condenser and the capillary (or expansion valve) .

Liquid storage tank: during the operation of the refrigeration system, the circulating amount of refrigerant in the system will change due to the change of working conditions or the adjustment of refrigerating capacity. Setting up a liquid storage tank can make use of the liquid storage capacity of the liquid storage tank, balance and stabilize the amount of refrigerant circulation in the system. In addition, when some parts of the refrigeration system failure needs to be repaired, through a certain method of operation, the system refrigerant back to the storage tank. The liquid storage tank is usually arranged between the condenser and the throttling element to enable the refrigerant liquid in the condenser to enter the liquid storage tank smoothly. The storage tank shall be positioned below the condenser. ELECTROMAGNETIC FOUR-WAY REVERSING VALVE: its principle is simple: solenoid coil electrify, change the valve block in the direction of action, change the direction of refrigerant flow. For Cooling or heating purposes. SOLENOID VALVE: solenoid valve is usually installed in front of the expansion valve, used to directly control the amount of refrigerant into the evaporator. Can also be installed in the compressor before unloading cylinder, control compressor cylinder unloading. Divided into two: Direct Open and close type solenoid valve; indirect type solenoid valve. One-way Valve: The one-way Valve is usually connected in parallel with the auxiliary capillary, and the two are connected in series with the main capillary. A check valve is a tubular element with a spherical or hemispherical plug of movable stainless steel or nylon material. Combined with capillary tube, it can adapt to two different operating conditions of refrigeration and heating. 5. The types and status of refrigerants are R22, R410A and R32. R22 is a medium temperature refrigerant, the standard for-40.8 degrees of water in R22 solubility is very small, and mineral oil mutual dissolution, R22 does not burn, does not explode, very small toxicity, permeability. R410A is a kind of HFC refrigerant which is made up of R32 and R125 by mixing two working substances at 50% and 50% mass fraction. The source of this article is Refrigeration Encyclopedia Public No. , which is a near azeotropic mixture, and its thermodynamic properties are very close to the single working substance. Compared with R22, R410a is a high pressure refrigerant with 1.6 times higher condensing pressure, so it is necessary to improve the system pressure strength. R32, short for Difluoromethane, is a zero Ozone depletion potential refrigerant, which is a gas at room temperature, a colorless transparent liquid at its own pressure, easily soluble in oil, difficult to dissolve in water, and is an energy saving, carbon reduction, environmental protection and non toxic refrigerant, but flammable and explosive!
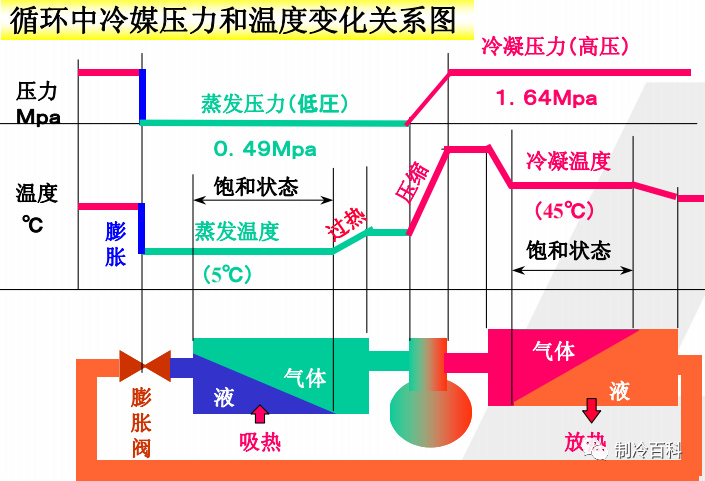
The three states of refrigerant: Saturated, superheated, supercooled saturated refrigerant: Saturated Refrigerant in the vapor-liquid conversion in the state of equilibrium, at this time the liquid, gas in the saturated state.
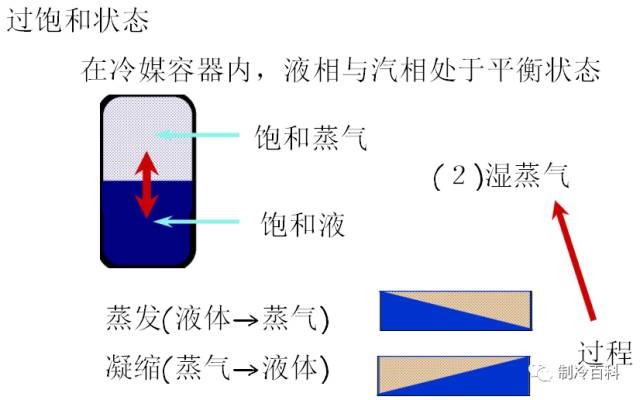
The three states of refrigerant: Saturated, superheated, supercooled saturated refrigerant: Saturated Refrigerant in the vapor-liquid conversion in the state of equilibrium, at this time the liquid, gas in the saturated state.

Near the outlet of the evaporator, the refrigerant continues to absorb heat after complete evaporation and becomes superheated refrigerant with temperature higher than saturation temperature.

Subcooled refrigerant: The liquid temperature of the refrigerant in the subcooled refrigerant is lower than the saturation temperature under the corresponding saturation pressure, and supercooled only when there is no steam in the fluid refrigerant. There is no one-to-one relationship between temperature and pressure of refrigerant liquid under undercooling. In between the condenser outlet and the throttle valve, the refrigerant condenses into a saturated liquid and may continue to exothermic cooling and become a supercooled refrigerant.

Article Collation from the "encyclopedia of refrigeration"
cold and warm life, Binger accompanied -
 Analysis of operation parameters and working condition of water chiller 2020-04-01
Analysis of operation parameters and working condition of water chiller 2020-04-011.Evaporation pressure and evaporation temperature, in the operation of chillers, evaporation temperature, evaporation pressure and cold water into the heat evaporator is closely related. When the heat load is large, the return water temperature of the cold water of the evaporator rises, which causes the temperature of the evaporator to rise and the corresponding evaporation pressure to rise. On the contrary, when the heat load is reduced, the return water temperature of cold water decreases, and its evaporation temperature and evaporation pressure both decrease. When the heat load of the air-conditioned room is reduced, the return water temperature of the cold water decreases, and the evaporation temperature and evaporation pressure are evenly distributed. According to the standard of JB / T3355 -- 1998, the rated working condition of chiller is 7 °C of chilled water outlet temperature and 30 °C of cooling water return temperature. The other corresponding parameters are the return water temperature of freezing water 12 °C, and the outlet water of cooling water 35°C.

2.According to the National Standard GB / T18403.1 -- 2001, the rated working conditions of chillers are chilled water inlet and outlet temperature 12 °C / 7 °C and cooling water inlet and outlet temperature 30 °C / 35 °C. Therefore, when the chiller leaves the factory, the working conditions are the inlet and outlet temperature of the chilled water 12 °C / 7 °C and the inlet and outlet temperature of the cooling water 30 °C / 35 °C. In operation, the temperature of cold water should be raised as much as possible when the requirement of air conditioning is met. In general, the evaporation temperature is 2 °C ~ 4 °C lower than the cold water outlet temperature. The evaporation temperature is usually controlled in the range of 3 °C ~ 5 °C. Too high evaporating temperature is difficult to achieve the required air conditioning effect, and too low evaporating temperature, not only increases the unit's energy consumption, but also easy to cause the evaporating pipeline freeze crack.

3.Condensation pressure and condensation temperature in a chiller, the pressure indicated by a high-pressure gauge is called condensation pressure, and the temperature corresponding to the pressure is called condensation temperature. The condensing temperature is of great importance to the power consumption of the unit under the condition of constant evaporating temperature. In addition, the increase of the condensing pressure of the centrifugal refrigeration unit will cause the surge of the main engine. On the contrary, the power consumption decreases with the reduction of condensation temperature. Therefore, in the operation of chillers, attention should be paid to ensure that the cooling water temperature, water quantity, water quality and other indicators in the eligible range. When the air is in the condenser, the temperature difference between the condensing temperature and the cooling water outlet increases, while the temperature difference between the cooling water inlet and outlet decreases. In addition, scaling and sludge on the water side of condenser tubes also play an important role in heat transfer. 3. Pressure and temperature of cold water chillers for air conditioning generally operate under the conditions of 12 °C of cold water return water temperature, 7 °C of water supply temperature and 5 °C of temperature difference stipulated in the standard working conditions. The cold water flow rate of the evaporator is inversely proportional to the temperature difference between supply and return water, that is, the larger the cold water flow rate, the smaller the temperature difference;. Therefore, the operating condition of the chiller sets the temperature difference between the cold water supply and return water as 5 °C, which in fact sets the cold water flow rate of the chiller. This control of the flow of cold water on the performance of the control of cold water through the evaporator too much pressure drop. The pressure drop of cold water supply and return water on the evaporator is set to 0.5 KGF / CM2 under standard operating conditions. The pressure drop adjustment method is to adjust the cold pump outlet valve opening, and evaporator supply, backwater valve opening.
4.The pressure and temperature of cooling water chillers run under standard operating conditions, the return water temperature of the condenser is 30 °C and the outlet temperature is 35 °C. For Water chillers in operation, environmental conditions, loads and refrigerating capacity have been established. At this point, the condensation heat load is no doubt constant. The standard stipulation enters, the water temperature difference is 5 °c, the cooling water flow must also be certain value. And the flow is inversely proportional to the difference in temperature between the incoming and outgoing water. Therefore, chillers in standard operating conditions, as long as the provision of cooling water into and out of the water temperature difference on the line. This flow is usually controlled by the pressure drop of cooling water in and out of the condenser. Under standard operating conditions, the outlet pressure drop of the condenser is set at about 0.75 KGF / CM2. Pressure drop adjustment method is also used to adjust the cooling water pump outlet valve opening and condenser inlet and outlet valve opening. In order to reduce the power consumption of water chiller, the condenser temperature should be as low as possible. It can take two measures: reducing the return water temperature of the condenser and increasing the cooling water. For Centrifugal chillers, too high or too low condensation pressure will cause surge. Centrifugal chillers encountered in this case, should pay attention to the condensation pressure and evaporation pressure difference can not be too small, should meet the need to prevent the occurrence of surge, otherwise there will be surge. In the autumn when the temperature is low, it is advantageous to run the reciprocating chillers because the condensing pressure is low and the power consumption is greatly reduced.
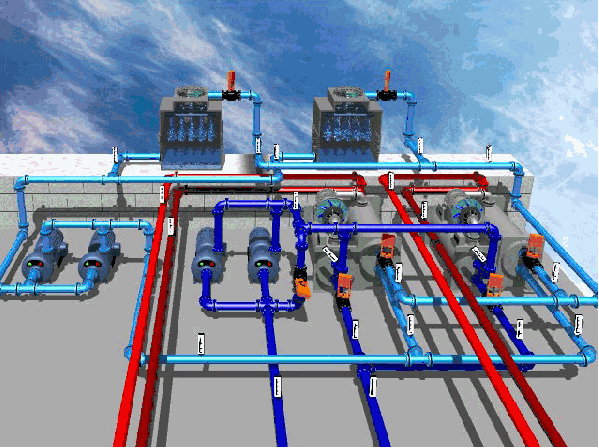
5.Compressor suction temperature the suction temperature of a compressor, for Reciprocating compressor, is the temperature of refrigerant gas in the Suction Chamber of the compressor; for Centrifugal compressors, it is the temperature of refrigerant gas on the Suction Guide vanes. The suction temperature not only affects the exhaust temperature, but also has an important impact on the volumetric refrigeration capacity of the compressor. When the compressor suction temperature is high, the exhaust temperature is high, the refrigerant is inhaled when the specific volume, when the compressor unit volume refrigeration capacity is small, this is what we do not want. In contrast, the compressor suction temperature is low, its unit volume refrigeration capacity is large. However, the compressor suction temperature is low, may result in refrigerant liquid was divided compressor suction, so that the Reciprocating compressor "liquid shock" . And for centrifugal compressor, because of too low suction temperature so that the compressor suction pressure is too low, may produce surge. Therefore, to provide for the compressor suction superheat. For reciprocating chillers, the compressor suction superheat for 5 ~ 10 °C, when the use of dry evaporator. The degree of superheat can be controlled by a thermal expansion valve, and the degree of superheat can be adjusted by adjusting the adjusting screw rod of the thermal expansion valve. 6. The exhaust temperature of the compressor is much higher than the condensing temperature, the direct influence factor of the exhaust temperature is the suction temperature of the compressor, the two are proportional. If the Reciprocating compressor suction, exhaust valve plate is not tight or broken leakage (internal leakage) , the exhaust temperature will rise significantly. In the centrifugal refrigeration unit, if the refrigeration system mixed with air, the suction temperature and exhaust temperature will increase. The middle pressure and temperature of the chiller is called the economizer, and the pressure inside the economizer is the middle pressure of the chiller, the refrigerant temperature is the intermediate temperature and the intermediate pressure is determined by the principle that the total power consumption of the low-pressure and high-pressure stage compressors of the two-stage centrifugal refrigeration compressor is as small as possible and the circulating refrigeration system is as large as possible. 8. Oil pressure difference, oil temperature and oil level high lubricating oil system is an indispensable part of the normal operation of the unit, which provides lubrication and cooling conditions for the moving parts of the unit. The oil pressure difference, oil temperature and oil pressure height are the three essential factors to ensure the lubrication and cooling of moving parts under normal working conditions. The ROLE OF OIL PRESSURE DIFFERENCE: is to make the oil in the oil pump drive, in the oil system pipeline flow, transport to the working parts to overcome its flow resistance. Oil Temperature: The oil temperature has an important influence on the viscosity of lubricating oil. Low Oil temperature will increase the oil viscosity, liquidity, not easy to form a uniform oil film, can not achieve the desired lubrication effect. Oil Level: The oil level is too low easy to cause the unit operation failure or damage accident. REFERENCE FOR CONTROL RANGE OF OIL PRESSURE DIFFERENCE: Reciprocating unit is 1.5 ~ 3.0 KGF / CM2; twin screw unit is 1.5 ~ 12.5 KGF / CM2; Centrifugal unit is 1.5 ~ 2.5 KGF / CM2. 9. Unit operating current and voltage the rated supply voltage required by general unit is 380V, three-phase, 50Hz, the average phase voltage instability rate is less than 2% . The operating voltage of all motors shall be within 5% of the voltage specified on the compressor nameplate.
Article Collation from the "encyclopedia of refrigeration"
cold and warm life, Binger accompanied -
 Operating parameters of air conditioning water system and refrigeration system 2020-03-18
Operating parameters of air conditioning water system and refrigeration system 2020-03-18Unit Working Power Supply Unit working power supply is 380V / 50Hz / 3n, its fluctuation range is between 360V ~ 420V. However, the operation of the unit has strict requirements on power supply: Power supply three-phase voltage imbalance should not be greater than 2, power supply three-phase current imbalance should not be greater than 10. Voltage is too high or too low, will cause the unit motor running current is too large, serious will burn out the unit motor.

Three-phase voltage unbalance calculation method: For example, the unit rated voltage is 380V, the measured three-phase voltage is: A-B 386V; A-C 385; B-C 382V; namely 386-3806,385-3805,382-3802. Three-phase voltage imbalance 63801001.6, that is normal (three-phase current imbalance calculation method is the same) . 2. The operating parameters of circulating water system should check the pressure difference between the inlet and outlet of chilled water and cooling water before starting up, which should be between 0.08 MPA and 0.15 MPA. If the inlet pressure is 0.4 MPA, the outlet pressure should be between 0.32 MPA and 0.25 MPA. The pressure difference is too small, that unit water flow is not enough, at this time, we should check whether the pump is working properly, whether the valve is open normally, whether the water system has air, whether the water system filter (y grid) is blocked, etc. . Do not turn on the machine until the water supply is confirmed to be normal. If the water supply is not normal, the unit will not be long after the start-up "low evaporation temperature" alarm and protective shutdown. During the normal operation of the unit, we should pay attention to the temperature difference between the inlet and outlet of the chilled water and the cooling water, which should be between 3 °C and 5 °C. If the temperature of the frozen water inlet is 15 °C, the temperature of its outlet water should be between 12 °C and 10 °C. If the temperature difference is too small, the heat exchange effect of the heat exchanger of the unit is poor. At this time, we should check whether the water quality is normal, whether the heat exchange pipe is dirty and dirty, and so on, we should check whether the normal operation of the pump, the opening of the valve is normal, whether the water system has air, water system on the filter (y grid) is blocked, etc. . Time is not long the unit will be "low evaporation temperature" alarm and protective shutdown. We should pay attention to observe the difference between the outlet temperature of chilled water and cooling water and the refrigerant temperature of evaporator and condenser should not be more than 2.5 °C. If the outlet temperature of the freezing water is 10 °C, the outlet temperature of the evaporator should be between 8 °C and 10 °C, and the outlet temperature of the cooling water should be between 30 °C and the outlet temperature of the condenser should be between 28 °C and 30 °C. The smaller the temperature difference is, the better the heat exchange effect of the unit heat exchanger is. The larger the temperature difference is, the worse the heat exchange effect of the unit heat exchanger is.
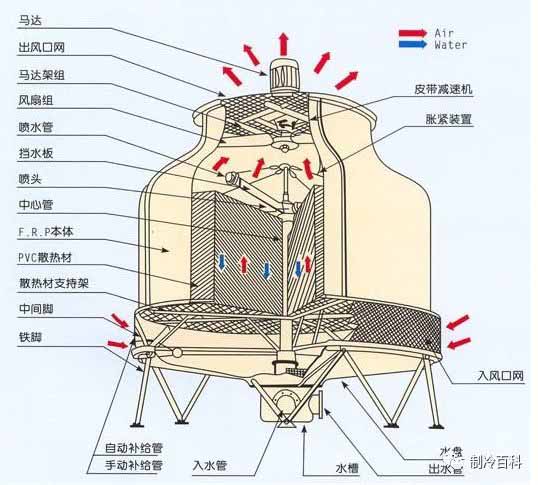
We should pay attention to observe the temperature difference between the inlet and outlet water of the Cooling Tower, which should be between 3 °C and 5 °C. If the inlet water temperature of the cooling tower is 30 °C, the outlet water temperature of the cooling tower should be between 25 °C and 27 °C. The temperature difference is too small, that the cooling tower cooling effect is poor. In another case, when the inlet temperature of the cooling tower is higher than the ambient temperature, the difference between the ambient temperature and the outlet temperature of the cooling tower should not be more than 3 °C. If the ambient temperature is 34 °C and the inlet water temperature of the cooling tower is 37 °C, the outlet water temperature of the cooling tower is about 34 °C. At this time, higher than our unit normal operating temperature requirements, we do not think that the cooling tower cooling effect is not good, in fact, this is normal. Because the cooling tower itself does not have the function of cooling, it is only the auxiliary cooling water to the environment space, so the water temperature of the cooling tower is close to the environment temperature, it should be the best working state of the cooling tower. Three, refrigeration system's main parameter refrigeration system's debugging is adjusts the system operation parameter to the request scope. The main parameters of refrigeration system are: evaporating temperature and pressure; condensing temperature and condensing pressure; compressor suction and exhaust temperature; compressor suction and exhaust pressure; oil temperature; oil filter pressure difference. These operating parameters are not fixed, but change with the change of the external conditions. Therefore, when the refrigeration unit is debugged, the operating parameters must be adjusted according to the external conditions and the characteristics of the unit so that they can operate under reasonable, economical and safe values. Evaporation temperature and pressure the evaporation temperature and pressure are determined according to the user's requirements. The evaporating temperature of the unit should be determined according to the temperature requirement and working characteristics of the cooling medium. For the refrigeration capacity of the compressor, when the condensing temperature is fixed, the lower the evaporating temperature, the smaller the refrigeration capacity, due to insufficient cooling capacity, so that the cooling medium temperature can not be reduced. While the temperature difference is smaller, the heat transfer effect is poor, although the compressor cooling capacity increases, but the evaporator heat exchange is not sufficient. Therefore, we should choose the temperature difference reasonably according to the different forms of refrigeration equipment. According to the standard of JB / T4329-97 volumetric cold water (heat pump) units in China, the nominal working conditions of chillers are cold water inlet temperature 12 °C, outlet water temperature 7 °C, cooling water inlet temperature 30 °C and outlet water temperature 35 °C.

As a result of increasing the temperature of the cold water out of the unit is very beneficial to the economy. In operation, the temperature of cold water should be raised as much as possible when the requirement of air conditioning is met. If the cold water outlet temperature is not 7 °C for long term operation, the required cold water outlet temperature should be specified in the contract. Therefore, in the actual operation of the unit, according to the specific requirements of the air-conditioning object, the cold water temperature can be raised or appropriately lowered. In general, the evaporation temperature is 2 ~ 4 °C lower than the cold water outlet temperature, then the evaporation temperature is controlled in the range of 3 ~ 5 °C. For evaporators with cooled liquid medium, the evaporating temperature should be 4 ~ 6 °C lower than that of the cooled liquid medium. The difference between the evaporating temperature and the temperature of the cooling medium is actually the opening of the throttle valve. At present, there are commonly used throttle manual throttle, thermal expansion valve, constant pressure expansion valve, float ball valve, etc. . When we debug and run, we mainly observe the change of evaporation pressure to judge whether the expansion valve opening is suitable. If the valve opening is too small and the liquid supply is insufficient, the evaporating pressure and temperature will drop, the compressor will draw in too hot, the exhaust temperature will also rise, and if the liquid supply is too much, the evaporating pressure and temperature will both rise, and the excessive liquid, it will also cause the compressor to have the liquid strike accident. Therefore, it is one of the main methods to control the evaporation temperature and pressure in operation to control the opening degree of the throttle valve correctly. In addition, if the heat exchange area of the evaporator is too small or if there is dirt on the inner and outer surfaces, the evaporation temperature will be reduced when the cooling load and the capacity of the compressor are not changed, then the evaporating temperature 2, condensing temperature and condensing pressure of the refrigeration system are the pressure indicated by the high-pressure gauge. Under normal circumstances, the condensing temperature is 5-7 °c higher than the inlet temperature of the cooling water, it is 10 ~ 15 °c higher than the inlet temperature of cooling air with forced ventilation. When the evaporating temperature is constant, the condensing temperature and pressure increase, the compressor compression ratio increases, the gas transmission coefficient decreases, the refrigeration capacity of the compressor decreases, but the power consumption increases. In addition, the condensation pressure increases, the compression exhaust temperature increases. If the exhaust temperature is too high, it will dilute the compressor lubricating oil and affect the lubrication. When the exhaust temperature is close to the lubricating oil valve point, some lubricating oil will be carbonized and accumulate in the exhaust valve, which will affect the sealing performance of the valve, on the valve plate, end cover spring and so on have an impact. During the operation, the heat transfer resistance is increased and the refrigerant vapor can not be condensed in time because of the non-condensable gas such as oil film, scale on the inner surface of the condenser or a little air in the system. The general treatment method is to regularly drain oil, air and according to the water quality of regular cleaning scale. There are two ways to clean and remove the scale and reduce the condensing temperature: to reduce the water temperature of the condenser cooling water and to increase the cooling water. 3. The suction temperature and suction pressure of the compressor suction temperature is high, the exhaust temperature is also high, the specific volume of the refrigerant when it is inhaled is large, when the refrigeration capacity per unit volume of the compressor is reduced; on the contrary, when the suction temperature of the compressor is low, the refrigeration capacity per unit volume is large. But the compressor suction temperature is too low, may cause the refrigerant liquid was sucked into the compressor, so that the Reciprocating compressor produced a liquid hit phenomenon. In addition, the length of the compressor suction pipe and wrapped insulation material performance, the size of the superheat, but also have a certain impact. The suction temperature is generally controlled at 5 ~ 10 °C in the refrigerating unit, and 15 °C in the freon system with the regenerative heat exchanger. Therefore, in the operation of the machine, we must pay attention to the control of the suction temperature of the compressor, usually with the adjustment of the thermal expansion valve screw to adjust the size of the overheating. 4, compressor exhaust temperature and pressure compressor exhaust temperature is the refrigerant after compression of high-pressure superheated steam. Because the refrigerant discharged by the compressor is superheated steam, there is no corresponding relationship between its pressure and temperature. The exhaust temperature of the compressor can be read from the thermometer on the exhaust pipe. The exhaust pressure is generally slightly higher than the condensation pressure and the exhaust temperature is much higher than the condensation temperature. The exhaust temperature is mainly related to the suction temperature, pressure and pressure ratio, and increases with the increase of them. Condensing temperature and exhaust temperature are too high on the operation of the compressor is unfavorable, should be prevented. 5. The normal oil temperature of oil temperature unit is between 45 °C and 68 °C. If the oil temperature is too low, a large number of refrigerant will dissolve in the oil, will cause the unit to return oil difficult, a large number of oil in the evaporator and condenser, affect the heat transfer effect. At this point we have to adjust the oil cooler supply (water) valve to maintain the appropriate oil temperature. If the oil temperature is too high, it will reduce the viscosity of the oil, lose its lubricating effect and shorten the service life of the spare parts of the unit. At this point, we want to check whether the oil cooler supply (water) valve open normal or oil cooler supply (water) pipeline is blocked, for removal. 6, oil filter pressure difference should be less than 50 PISD. If the pressure difference is greater than 50Pisd, the unit will be "oil filter blockage" alarm and protective shutdown. It indicates that the oil filter of the unit is saturated or dirty. At this point, we need to replace the oil filter, to ensure that the normal oil supply unit.
Article Collation from the "encyclopedia of refrigeration"
cold and warm life, binger accompanied! -
Precautions for R410A refrigerant used in air conditioning 2020-02-17
1. Please do not mix with other refrigerant and refrigeration oil. R410A special tools are mainly used for after-sales service. Unlike air conditioners using other refrigerants, do not mix them.
2. The pressure of R410A is about 1.6 times higher than that of R22 refrigerant. Once the wrong operation occurs in the process of construction and after-sales service, a major accident may occur. When installing air conditioner with R410A refrigerant, use R410A special tools and materials,.
3. Different from other refrigerants used before, it is easy to be affected by impure substances such as moisture, oxide layer, grease, etc. Therefore, full attention shall be paid to the use of clean piping to prevent moisture from mixing in during construction operation.
4. From the point of view of protecting atmospheric environment, vacuum pump is needed. R410A is a kind of azeotropic mixed refrigerant, which is added by liquid way. When the gas is added, the composition of the refrigerant will change.
5. Before installation, first confirm the name of air conditioner refrigerant, and then carry out different operations for different refrigerant. In household air conditioners using R410A refrigerant, refrigerant other than R410A must not be used. In the air conditioner using R22 refrigerant, R410A refrigerant should not be used.
6. When installing or moving the air conditioner, please do not mix air other than R410A refrigerant into the refrigerant circulation pipeline of the air conditioner. If air and other non condensable gases are mixed in, it will lead to abnormal high pressure in the refrigerant circulation pipeline, which is the main reason for the cracking of the circulation pipeline.
7. After the installation, please carefully confirm that there is no refrigerant leakage. If the refrigerant leaks in the room, once it contacts with the electric sparks from the electric fans, heating furnaces, electric furnaces and other appliances, toxic gases will be formed.
8.In case of refrigerant leakage during operation, please ventilate in time. When installing the air conditioner with one drag and more air conditioners, for example, the amount of refrigerant sealed in is relatively large, especially in the small room. Even in case of refrigerant leakage, its concentration cannot exceed the specified value. Otherwise, it will cause anoxia.
Article arrangement comes from "refrigeration encyclopedia"
Warm and cold life, accompanied by ice!
-
Common problems and maintenance of air source heat pump 2020-01-16
Compressor blocking and turning from the anatomical phenomenon of most fault compressors, there is no lack of oil inside the compressor, holding the shaft blocking and turning is caused by poor instantaneous lubrication, and the main reason leading to poor lubrication is the change of lubricating oil quality, the oil is diluted or the oil level is raised by the refrigerant liquid.
Compressor pure motor burn two reasons:
Motor temperature rise is too high;
the refrigeration system is not clean inside.
Motor temperature rise is too high: When Heat pump mechanism is hot in winter, the working condition is quite bad, especially when the environment temperature is very low, the heat exchange quantity is very small, the refrigerant circulation quantity is also small, the return air pressure is low, in addition to the electric control defrosting is not prompt and thorough, will lead to inadequate motor cooling, coil heating, insulation damage, Motor short-circuit burn-out. The refrigeration system is not clean: in addition, the refrigeration system is not clean, contains impurities, impurities corrosion and wear motor coil, resulting in short-circuit burn.
3, communication failure reason analysis: check whether the four core wire of the electronic control motherboard and the panel is in good contact; check whether there is 12V power output, voltage is too high or too low; check whether the panel itself is in trouble; check whether the panel and the motherboard are matched; Keep the power from interfering with communications.
4, water temperature, environment, defrosting, backwater temperature sensor failure reason analysis: check whether the temperature sensor line is broken or damaged phenomenon; check whether the Sensor Resistance is normal; check whether the sensor resistance is bad.
5, water flow failure reason analysis: check whether the pump is open and whether there is air in the pump; check whether there is water in the tank; check whether the water flow switch is damaged; check whether the water flow switch two lines to the motherboard in good contact.
6, high-pressure protection reason analysis: Check whether the unit is really high-pressure protection in operation; check whether the high-pressure protection failure check whether the pump is air, whether the water pipe filter is blocked; check whether the unit system is blocked, mainly expansion valve, capillary, filter; check whether the high-voltage switch is broken; check whether the two lines connecting the high-voltage switch on the electronic control board are in good contact; check whether the high-voltage function of the Electronic Control Board is invalid.
7, low-voltage protection reason analysis: Check whether the refrigerant leak; check whether the low-voltage meter operation is really low-voltage protection; check whether the unit system expansion valve, capillary, filter plugging; Check whether the two lines connected with the low-voltage switch on the Electronic Control Board are in good contact; check whether the low-voltage function of the Electronic Control Board is invalid; check whether the system is leaking cold medium.
8, three-phase protection (phase sequence error, missing phase, current is too large) reason analysis: check the unit power three-phase missing phase; phase sequence board on the two lines to the main board terminal contact is good; check the voltage is too low, power line capacity is not enough, especially the case of a very long power cord
9, power but the motherboard and panels are not power cause analysis: check the motherboard power terminal wire and zero wire between whether there is 220V power; check the motherboard on the fuse has burned; Check the transformer and see if the three terminals on the transformer connection motherboard are plugged in;
10, power switch trip cause analysis: If a trip on the power supply line leakage, short circuit, grounding phenomenon check whether make-up Valve, backwater valve, water valve, one of a work jump;
11, water temperature does not rise reason analysis: check whether there is leakage of fluoride, observe the high and low pressure of the unit; check whether the amount of water exceeds the unit's water output; check whether the unit's circulating pipe, water supply hot water pipe, return water pipe insulation effect is good; Check whether the unit is equipped with small, especially the temperature control backwater project in winter low temperature backwater this piece to lose a large part of the heat to supply.
12, defrosting problem reason analysis: check whether the defrosting probe is faulty; check whether the defrosting probe and evaporator are in good contact, the position is very correct; check whether the defrosting probe is invalid; Check if there is any problem in setting parameter .
13, cause analysis of the unit not running: check the power supply failure to disconnect the power supply switch, check the power supply; check the power supply loose to disconnect the power supply switch, check the power supply; check the Unit to control the power supply fuse to fuse, find out the cause and fix it, replace the new fuse.
14, pump operation but the water does not cycle or pump noise big reason analysis: water shortage inspection system in the water supply system replenishment device, and to the system water replenishment; Check the water system valve all open, the Water System Valve open full; check water filter dirty block, clean water filter.
15, unit heating capacity on the low cause analysis: check whether the refrigerant is insufficient, the system leak detection and filling of refrigerant; check whether the water system insulation is bad, strengthen the water system insulation; check whether the drying filter is blocked, replace the drying filter; Check whether the air heat exchanger is poor, clean the air heat exchanger; check whether the water flow is insufficient, clean the water filter.
16, the compressor does not run reason analysis: check whether the power supply failure, find out the reason to solve the power supply failure; check whether the wiring is loose, find out the point of looseness and repair; check whether the compressor overheating protection, find out the cause of heat after troubleshooting before starting; Check if the water temperature is too high, reset the water temperature; check if the water flow is insufficient, clean the water filter to remove air from the system.
The collation comes from the "encyclopedia of refrigeration, "
Cold and warm life, accompanied by binger
-
 How to deal with the compressor cylinder jam? 2020-01-13
How to deal with the compressor cylinder jam? 2020-01-13Compressor cylinder is stuck compressor shaft is stuck, the compressor can not rotate at this time. The reason that the compressor causes the cylinder to jam is either the frozen oil does not come up, so that the lubrication is insufficient, the friction increases, or the pipe has the dust, the impurity, causes the moving surface to jam, or the pure mechanical breakdown causes the compressor to jam.
Treatment method of compressor cylinder jam
The percussive method
Choose a wooden hammer or select the available items in place. When the press starts, the hammer hits the three welds on the body. But pay attention to the force. Don't break the shape. Gently tap the compressor casing to loosen the stuck part, sometimes it can start operation or increase the power supply voltage by 10% , multiple start-up shock, this method can solve the problem of not enough lubrication stuck cylinder, especially effective for rotary compressors.
Two, strong up method
Connect a plug, l directly connected to the C terminal, N connected to the M terminal, another out of the branch line N1, turn on the power so that N1 touch the starting end of the compressor S.
Capacitance starting method
Increasing the capacity is one of the most common methods, simply put on the original capacitor and a capacitor or change a larger capacitor, to increase the starting Torque to make the compressor easier to operate. Note: The compressor started two or three seconds immediately shut down.
Pressure relief method also known as decompression method
Release some of the Freon to reduce the pressure, and then use the above methods, comprehensive utilization.
Pneumatic shock method
Remove the compressor from the high pressure pipe and use nitrogen to give the compressor a 0.1 MPA reaction. Make hold the axle parts loose. Five minutes of air. Then apply the above methods.
Three-phase power start method
Above all do not work, can use three-phase power start method, connect method is n to connect C. R and s are connected to different firing lines. Plug-in short time to start within 6 seconds.
Lubrication method
Usually the compressor internal oxide skin, or dirt caused by the card cylinder, the above can not work, the compressor removed, the oil out. Add Kerosene, and then pour it out again, one time, the goal is to wash out the dirty things inside, clean and then put the compressor upside down for 12 hours, the kerosene, and volatile. Then add 25 frozen oil, pick up the compressor and then in the ground pier a few times, so that the machine loose. Before using the above method to activate.
Repair Ok to add R22 frozen oil, the effect will be much better. The above methods are flexible use of a lot of compressors can be repaired, if the compressor resistance is normal.
The collation comes from the "encyclopedia of refrigeration, "
Warm and cold life, Binger company!


