News Center
- Air Conditioning maintenance debugging must master the basic knowledge, these you understand? Oh, Shit
- date: 2020-04-10 hits:682
Air Conditioning maintenance debugging must master the basic knowledge, these you understand? Oh, Shit
here are many methods of refrigeration, commonly used are: gas expansion refrigeration, liquid gasification refrigeration, vortex tube refrigeration and thermoelectric refrigeration. Liquid gasification refrigeration is the most widely used, its working principle is the use of liquid gasification endothermic to achieve refrigeration. 1. Working principle of air conditioning (mainly refrigeration, heating the opposite) : The high temperature and high pressure refrigerant discharged from the compressor flows through the four-way valve ——— The refrigerant is transformed from a gas state to a liquid state, through a capillary (or solenoid) throttling and pressure-reducing single-way valve (outdoor high pressure pipe) , the refrigerant enters a chamber heat exchanger (realizing refrigeration) . Complete a single-loop refrigeration cycle.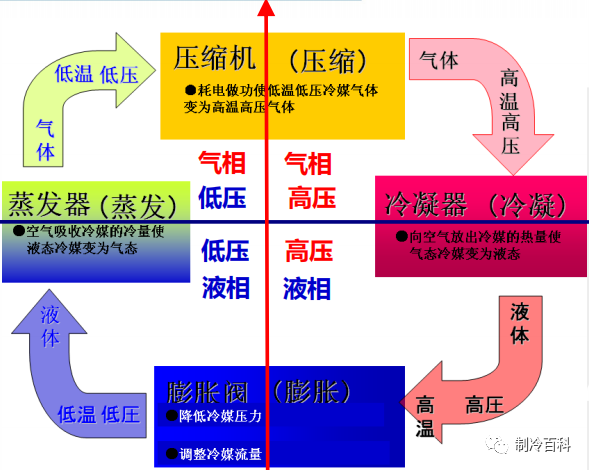
2, refrigeration system components: air conditioning refrigeration system is mainly composed of four major components and some auxiliary equipment in the refrigeration system. Four major parts are: compressor condenser throttling mechanism evaporator composition. Auxiliary Equipment: Oil Separator; drying filter; liquid storage tank; electromagnetic four-way Reversing Valve; solenoid valve; one-way Valve. 3. The working principle of each component compressor: as the "heart" of refrigeration system, it has important influence on the running performance, noise, energy consumption, vibration and service life of air conditioning. According to the thermodynamic principle, it can be divided into volume type and velocity type.
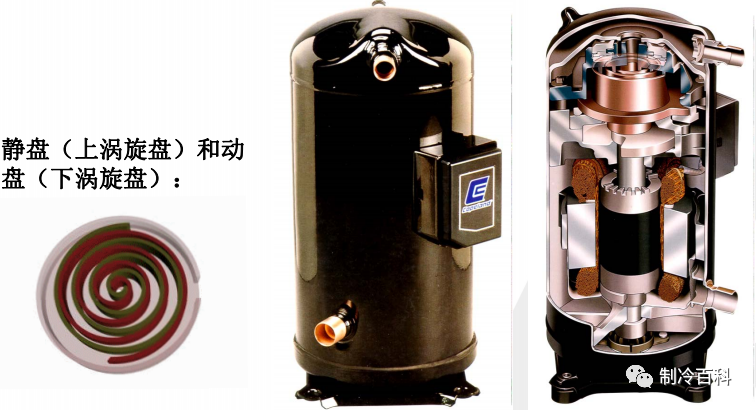

Volumetric type: A certain volume of gas inhaled into the cylinder and change the volume of the cylinder to achieve gas compression and forced discharge. Velocity type: The inhalation of gas to a certain speed, and then slow down, so that the kinetic energy into pressure and then out. The growth of the gas is due to the transformation of velocity. Scroll compressor: by The stator and Rotor two scroll body meshing from. Rotary compressor: by the eccentric wheel spindle, cylinder, sleeve, intake, skateboard, spring, exhaust valve, exhaust port composition. Condenser: the condenser is the refrigeration of the evaporator in the refrigeration system together with the power consumption of the compressor to the environment medium (cooling water or air) . According to cooling can be divided into air-cooled, water-cooled and evaporative. Cooling is mainly to the outdoor heat emission, heating to the outdoor absorption of heat. EVAPORATOR: The main function of the evaporator is to enter the throttle into the low-temperature and low-pressure refrigerant liquid boiling evaporation in the evaporator, absorbing the heat of the cooling medium, and then itself into a low-pressure saturated (usually some overheating) steam, it's being sucked away by the compressor. In other words, an evaporator is a heat exchanger that absorbs heat (i. e. outputs cold) . Throttling element: The throttling element is one of the four major components in the refrigeration system. Its main functions are: throttling and depressurizing the high-pressure liquid refrigerant, ensuring the pressure difference between the condenser and the evaporator, the refrigerant entering the evaporator is made to absorb heat and evaporate at low pressure under the requirement, thus achieving the aim of cooling down. Regulate the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator, so as to adapt to the load changes in the evaporator, so that the normal operation of the system.

CAPILLARY: a very thin tube, usually 0.5 ~ 2.5 mm in diameter and 1 ~ 5 M in length. When the refrigerant in the tube flow, the need to overcome the resistance in the tube, the natural generation of a certain pressure drop. Capillary features: Because in the normal state, when the compressor shutdown, high and low pressure can quickly balance, conducive to the compressor start again. The utility model has the advantages of simple structure, convenient manufacture and low price. For Heat pump systems, the refrigerant throttling process in the capillary tube, source: Refrigeration Encyclopedia Public, there is no import and export issues. In a capillary refrigeration system, the performance of the unit is very sensitive to the refrigerant charge. When the operating condition of the refrigeration system changes, the capillaries'ability to adjust the flow rate of refrigerant is poor. Because capillary inside diameter is small, conduit is long, be blocked easily, should notice system does not have inside dry with clean. Generally in front of the capillary tube set dry filter, in order to prevent blocking. Thermal Expansion Valve: the Control Valve that controls the amount of liquid supplied to the evaporator and is also the throttle valve of the refrigeration unit. Thermal expansion valve is the use of evaporator outlet refrigerant superheat changes to regulate the flow. According to the different structure can be divided into: Internal Balance and external balance. THERMAL EXPANSION VALVE DISADVANTAGES: Low Control Accuracy, Limited Adjustment Range, the valve body diaphragm deformation is limited, so that the change range of needle opening is small, so the flow of the adjustment range is small. Can Not be met when large flow regulation is required. The high temperature gas at the evaporator must first heat the shell of the temperature sensor, the shell of the temperature sensor has a large thermal inertia, resulting in the reaction lag electronic expansion valve: The application of the electronic expansion valve overcomes the shortcomings of the thermal expansion valve, it also provides the condition for the intellectualization of the refrigeration device. The electric signal produced by adjusting parameters is used to control the voltage or current applied to the expansion valve, so as to reach the goal of regulation. ELECTRONIC EXPANSION VALVE CLASSIFICATION: Electromagnetic Electronic Expansion Valve; electric electronic expansion valve. 4, Refrigeration System Auxiliary Equipment Oil separator: WORKING PRINCIPLE: compressor out of the high-pressure gas (gas and lubricating oil) , into the oil separator, into the oil separator will be separated from the working gas, down the inner wall of the cylinder. The working gas is drawn from the oil separator by a central tube through a perforated baffle. The separated oil, concentrated in the lower part of the oil separator, can be regularly discharged, or the use of floating ball valve, so that the oil automatically back to the compressor in the crankcase. DRYING FILTER: the role of the drying filter is to absorb water in the refrigeration system, blocking impurities in the system so that it can not pass, to prevent the refrigeration system pipeline ice block and dirty block. Since the most easily clogged part of the system is the CAPILLARY (or expansion valve) , the drying filter is usually installed between the condenser and the capillary (or expansion valve) .

Liquid storage tank: during the operation of the refrigeration system, the circulating amount of refrigerant in the system will change due to the change of working conditions or the adjustment of refrigerating capacity. Setting up a liquid storage tank can make use of the liquid storage capacity of the liquid storage tank, balance and stabilize the amount of refrigerant circulation in the system. In addition, when some parts of the refrigeration system failure needs to be repaired, through a certain method of operation, the system refrigerant back to the storage tank. The liquid storage tank is usually arranged between the condenser and the throttling element to enable the refrigerant liquid in the condenser to enter the liquid storage tank smoothly. The storage tank shall be positioned below the condenser. ELECTROMAGNETIC FOUR-WAY REVERSING VALVE: its principle is simple: solenoid coil electrify, change the valve block in the direction of action, change the direction of refrigerant flow. For Cooling or heating purposes. SOLENOID VALVE: solenoid valve is usually installed in front of the expansion valve, used to directly control the amount of refrigerant into the evaporator. Can also be installed in the compressor before unloading cylinder, control compressor cylinder unloading. Divided into two: Direct Open and close type solenoid valve; indirect type solenoid valve. One-way Valve: The one-way Valve is usually connected in parallel with the auxiliary capillary, and the two are connected in series with the main capillary. A check valve is a tubular element with a spherical or hemispherical plug of movable stainless steel or nylon material. Combined with capillary tube, it can adapt to two different operating conditions of refrigeration and heating. 5. The types and status of refrigerants are R22, R410A and R32. R22 is a medium temperature refrigerant, the standard for-40.8 degrees of water in R22 solubility is very small, and mineral oil mutual dissolution, R22 does not burn, does not explode, very small toxicity, permeability. R410A is a kind of HFC refrigerant which is made up of R32 and R125 by mixing two working substances at 50% and 50% mass fraction. The source of this article is Refrigeration Encyclopedia Public No. , which is a near azeotropic mixture, and its thermodynamic properties are very close to the single working substance. Compared with R22, R410a is a high pressure refrigerant with 1.6 times higher condensing pressure, so it is necessary to improve the system pressure strength. R32, short for Difluoromethane, is a zero Ozone depletion potential refrigerant, which is a gas at room temperature, a colorless transparent liquid at its own pressure, easily soluble in oil, difficult to dissolve in water, and is an energy saving, carbon reduction, environmental protection and non toxic refrigerant, but flammable and explosive!
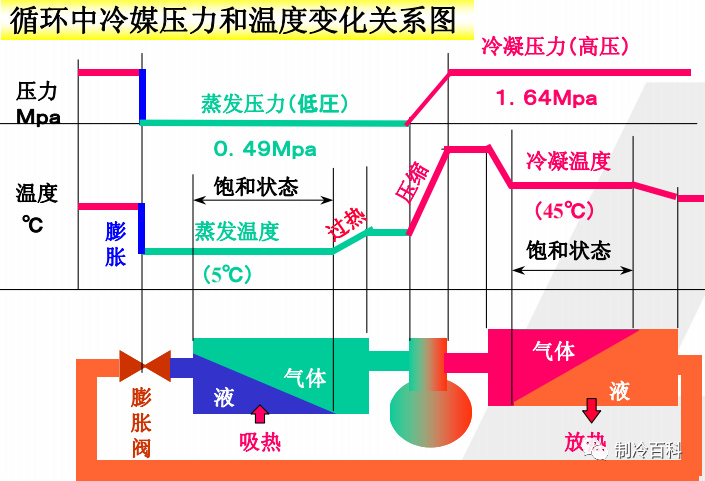
The three states of refrigerant: Saturated, superheated, supercooled saturated refrigerant: Saturated Refrigerant in the vapor-liquid conversion in the state of equilibrium, at this time the liquid, gas in the saturated state.
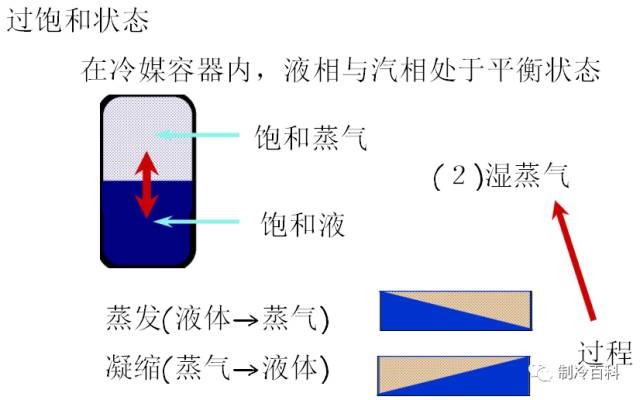
The three states of refrigerant: Saturated, superheated, supercooled saturated refrigerant: Saturated Refrigerant in the vapor-liquid conversion in the state of equilibrium, at this time the liquid, gas in the saturated state.

Near the outlet of the evaporator, the refrigerant continues to absorb heat after complete evaporation and becomes superheated refrigerant with temperature higher than saturation temperature.

Subcooled refrigerant: The liquid temperature of the refrigerant in the subcooled refrigerant is lower than the saturation temperature under the corresponding saturation pressure, and supercooled only when there is no steam in the fluid refrigerant. There is no one-to-one relationship between temperature and pressure of refrigerant liquid under undercooling. In between the condenser outlet and the throttle valve, the refrigerant condenses into a saturated liquid and may continue to exothermic cooling and become a supercooled refrigerant.

Article Collation from the "encyclopedia of refrigeration"
cold and warm life, Binger accompanied-
pre:Commercial Air conditioning co
next:Analysis of operation paramete - back


