News Center
-
Summary and analysis of 11 cases of air-conditioning water leakage 2021-04-22
Summary and analysis of 11 cases of air-conditioning water leakage
Cause Analysis: The newly installed air-conditioning room machine is leaking. After the machine is turned on and checked, it is found that after running for half an hour, the surface of the external drainage pipe about 2 meters long in the interior part is covered with water droplets. The office building is close to the river, and the environment humidity is very high, the Room is obviously larger and less enclosed, which leads to a lot of condensed water discharged from the inner side of the air conditioner. The Air condenses on the outer wall of the external drainage pipe because the external drainage pipe is only wrapped with a thin layer of tape.
Solution: Add a thermal insulation sponge on the outer wall of the external drainage pipe and re-wrap it. In the south humidity big area, the heat insulation thermal insulation sponge wrap must be in place. Case 8, drainage pipe broken leakage failure
phenomenon: internal machine leakage, start a period of time indoor machine has a large amount of water discharge, but outdoor drainage pipe did not condensate water discharge.
Cause Analysis: The main cause of water leakage is that the drain pipe and accessories connected with the water plate are damaged during installation or are bitten by mice during use.
Solution: replace the damaged drainage pipe, check whether there is a mechanism causing the damaged drainage pipe again and take appropriate protective measures.
Case 9, the system caused by fluoride leakage failure
phenomenon: air-conditioning operation for a period of time after the air-conditioning leakage, evaporator fin frosting or icing phenomenon.
Cause Analysis: The user reported that the internal engine was leaking, and after 10 minutes of on-site operation, found that the internal engine wind wheel began to blow water, the refrigeration mode continued to operate for more than 20 minutes, and found that there was a slight frost and ice on the fins near the input pipe of the evaporator, measuring System pressure with pressure gauge, the system pressure is very low 3KG, you can judge the system serious lack of fluoride.
Solution: Check the leak point, found that the connection pipe and low-pressure valve body connection misalignment lead to nut lock position leakage fluorine phenomenon, re-connect and lock, re-evacuation, add refrigerant after normal test machine.
Case 10, evaporator half leakage failure
phenomenon: Air Conditioning operation for a period of time after the air conditioning leakage.
Cause Analysis: After running for a period of time, the air conditioner leaked water. After 20 minutes of running, it was found that the air conditioner began to blow water. After opening the panel frame, it was found that the evaporator had several long U Tube Fins, which were very cold and had a lot of condensed water, the other evaporator fins were not obviously cool; the system was suspected to be deficient in fluorine, the system pressure was measured with a pressure gauge and the system pressure was normal; after a period of time, it was found that the long u-tube fins began to hang a lot of water and put their hands on the air outlet, it is found that the temperature difference between the fins of the two-stream U Tube is large, which can be used to judge the half-block of the evaporator and cause the deviation of the refrigerant When the evaporator is half blocked, the temperature of the Long U Tube Fin with large flow of snow species is lower, and the temperature of the Long U Tube Fin with small flow of snow species is higher, resulting in a large temperature difference between the two flow paths, the Long U Tube Fin with large flow of snow seeds condenses a large amount of condensed water and blows out with the wind.
Solution: Consult with the user after the replacement of the evaporator troubleshooting, for welding or semi-blocking system caused by partial flow heat exchanger condensation caused by the performance of a good distinction: the entire duct is full of fine water droplets, at the same time, water droplets can also be seen on the turbine blades.
Case 11, embedded air-conditioning leakage fault
phenomenon: internal leakage, running lights flashing.
CAUSE ANALYSIS: After inspection, the water directly overflows from the water disc, check the drainage pipe drainage, found that the water is very small preliminary judgment for drainage pump drainage is not enough, replacement of drainage pump test machine is normal. Solution: replace the drainage pump. The drainage method of the embedded machine is different from that of the split machine, which is natural drainage, while the embedded machine relies on the drainage pump. -
Common sense of using air conditioning in extreme rain and snow! 2021-02-23
Common sense of using air conditioning in extreme rain and snow!
At present, most mainstream brand air conditioners on the market have a minimum working temperature of -3°C to 7°C, and even some brands of heating outdoor units will freeze at 0°C! The editor below is going to zoom in! Offer the most professional extreme rain and snow weather air conditioner to use common sense to watch.
Common sense 1
Weather with low temperature and high humidity will increase the heat exchange and frosting of the outdoor unit of the air conditioner, and the heat exchange effect will be worse. Therefore, the heating effect of the air conditioner will decrease.Common sense 2
In order to ensure the normal operation of the air conditioner, the air conditioner itself has an automatic frosting function. The defrosting function, simply put, is a short "cooling operation" (the indoor unit does not blow out), allowing the outdoor unit to become a condenser for a few minutes, allowing the high-temperature refrigerant to defrost its own frost, and then automatically resume the system Hot running.Common sense 3
The defrosting process is automatic and cannot be controlled manually. In addition to causing the heating effect to decrease, it will also cause the indoor unit to have no hot air, the outdoor unit to emit white smoke (water vapor), the outdoor unit to flow black water, the venting sound (caused by the four-way valve switching), etc., these are all normal phenomenon.Common sense 4
Do not cut off the power supply of all air conditioners, and require continuous power supply to ensure that the outdoor unit crankshaft heater can continue to heat the compressor and ensure that the refrigerating oil does not freeze for good lubrication.Common sense 5
For air conditioners with a water system (multi-function VRV, etc.), please ensure that the power is supplied or take other measures according to the instruction manual. Otherwise, the protection function will not operate, and the low temperature below the freezing point may cause the water system to freeze. When the water freezes It will expand in volume and freeze the board, water pipe or fan coil.Common sense 6
The outdoor unit should be well ventilated to prevent the snow from burying the outdoor unit, and prevent the falling of snow from damaging the fan blades of the outdoor unit. Sometimes the snow can freeze the fan blades of the outdoor unit and cause the air conditioner to not work properly.Common sense 7
Air conditioners are high-current electrical equipment and should be powered separately, and all power cords should not have connectors. If there are connectors or sparks on the socket plugs, be sure to check and dispose of them. -
Common problems of after-sales maintenance of refrigeration units 2021-01-19
Common problems of after-sales maintenance of refrigeration units
1. Liquid back
1. For refrigeration systems using expansion valves, liquid return is closely related to the improper selection and use of expansion valves. Excessive selection of the expansion valve, too small superheat setting, incorrect installation of the temperature sensing bulb, damaged adiabatic dressing, and failure of the expansion valve may cause liquid flood back.
2. For small refrigeration systems that use capillary tubes, excessive liquid addition will cause liquid backflow.
3. When the evaporator is severely frosted or the fan fails, the heat transfer becomes poor, and the unevaporated liquid will cause liquid back.
4. Frequent temperature fluctuations in the cold storage will also cause the expansion valve to malfunction and cause liquid backflow.
For refrigeration systems where liquid return is difficult to avoid, the installation of a gas-liquid separator and the use of pump-down shutdown (that is, let the compressor drain the liquid refrigerant in the evaporator before shutdown) control can effectively prevent or reduce the harm of liquid return.
2.Start with liquid
1. When the return air cooling compressor is started, the phenomenon that the lubricating oil in the crankcase foams violently is called start with liquid.
2. The foaming phenomenon when starting with liquid can be clearly observed on the oil sight glass.
3. The root cause of starting with liquid is that a large amount of refrigerant dissolved in the lubricating oil and sinking under the lubricating oil suddenly boils when the pressure drops suddenly and causes the lubricating oil to bubble. The duration of bubbling is related to the amount of refrigerant, usually several minutes or ten minutes. A lot of foam floated on the oil surface and even filled the crankcase. Once sucked into the cylinder through the intake duct, the foam will be reduced to liquid (a mixture of lubricating oil and refrigerant), which can easily cause liquid hammer. Obviously, the hydraulic shock caused by starting with liquid only occurs in the starting process.
4. Unlike liquid flood back, the refrigerant that caused the start with liquid enters the crankcase by means of "refrigerant migration". Refrigerant migration refers to the process or phenomenon in which the refrigerant in the evaporator enters the compressor in gas form through the return line and is absorbed by the lubricating oil when the compressor stops running, or is mixed with the lubricating oil after being condensed in the compressor.
5. After the compressor is stopped, the temperature will decrease and the pressure will increase. Because the partial pressure of refrigerant vapor in the lubricating oil is low, it will absorb refrigerant vapor on the oil surface, causing the phenomenon that the crankcase air pressure is lower than the evaporator air pressure. The lower the oil temperature and the lower the vapor pressure, the greater the absorption power of refrigerant vapor. The steam in the evaporator will slowly "migrate" to the crankcase. In addition, if the compressor is outdoors, when the weather is cold or at night, its temperature is often lower than that of the indoor evaporator, and the pressure in the crankcase is also lower. After the refrigerant migrates to the compressor, it is easy to be condensed and enter the lubricating oil.
6. Refrigerant migration is a very slow process. The longer the compressor is down, the more refrigerant will migrate into the lubricant. This process will proceed as long as there is liquid refrigerant in the evaporator. Because the lubricant with dissolved refrigerant is heavier, it will sink to the bottom of the crankcase, and the floating lubricant can absorb more refrigerant. To
7. Due to structural reasons, the pressure of the crankcase will decrease much more slowly when the air-cooled compressor is started, the foaming phenomenon is not very severe, and the foam is difficult to enter the cylinder, so the air-cooled compressor does not have the problem of liquid hammering when starting with liquid. To
8. In theory, the installation of a crankcase heater (electric heater) on the compressor can effectively prevent the migration of refrigerant. After a short period of shutdown (such as at night), keeping the crankcase heater energized can make the lubricating oil temperature slightly higher than other parts of the system, and refrigerant migration will not occur. After a long period of shutdown (such as a winter), heating the lubricating oil for several or ten hours before starting up can evaporate most of the refrigerant in the lubricating oil, which can greatly reduce the possibility of liquid shock during startup with liquid It can also reduce the harm caused by refrigerant erosion. However, in practical applications, it is difficult to maintain the heater's power supply after shutting down or to supply power to the heater ten hours before starting up. Therefore, the actual effect of the crankcase heater will be greatly reduced. To
9. For larger systems, let the compressor drain the liquid refrigerant in the evaporator before shutting down (called pump-down shutdown), which can fundamentally avoid refrigerant migration. The installation of a gas-liquid separator on the return gas pipeline can increase the resistance of refrigerant migration and reduce the amount of migration. To
3. oil return
1. When the compressor is higher than the evaporator, the oil return bend on the vertical return pipe is necessary. The return bend should be as compact as possible to reduce oil storage. The spacing between the oil return bends should be appropriate. When the number of return bends is large, some lubricant should be added. To
2. The oil return pipeline of the variable load system must also be careful. When the load is reduced, the air return speed will decrease, too low speed is not conducive to oil return. In order to ensure the oil return under low load, the vertical suction pipe can adopt double vertical pipes. To
3. Frequent starting of the compressor is not conducive to oil return. Since the compressor stops for a short continuous operation time, there is no time to form a stable high-speed air flow in the return pipe, and the lubricating oil can only stay in the pipe. If the oil return is less than Ben oil, the compressor will be short of oil. The shorter the operating time, the longer the pipeline and the more complex the system, the more prominent the oil return problem.
4. Lack of oil will cause serious lack of lubrication. The root cause of the lack of oil is not the amount and speed of the compressor, but the poor oil return of the system. The installation of an oil separator can quickly return oil and extend the compressor running time without oil return.
5. The design of evaporator and return gas pipeline must take oil return into consideration. Maintenance measures such as avoiding frequent starting, timing defrosting, timely replenishment of refrigerant, and timely replacement of worn piston components also help to return oil.
4. Evaporation temperature/return air temperature/return air pressure
1. When the evaporation temperature increases by 10℃, the motor load can increase by 30% or even higher, causing the phenomenon of small horse-drawn carts. Therefore, if the low-temperature compressor is used in the medium-to-high temperature system and the cold storage cooling process lasts too long, the compressor will be overloaded for a long time, which will cause great damage to the motor, causing the motor to encounter unexpected situations such as voltage fluctuations and surges in the future. It is easy to burn at times.
2. The lower the evaporating temperature, the smaller the refrigerant mass flow, and the smaller the motor power actually required. Therefore, when air conditioning compressors and medium-high temperature refrigeration compressors are used at low temperatures, although the actual power consumption of the motor is much smaller than the nominal power, it is still too large compared to the actual power demand and cooling at low temperatures, and the motor cooling is easy problem appear. To
3. The return air temperature is relative to the evaporation temperature. In order to prevent liquid return, the return gas pipeline generally requires a return gas superheat of 20°C. If the return air pipe is not well insulated, the superheat will far exceed 20°C. To
4. The higher the return air temperature, the higher the cylinder suction temperature and exhaust temperature. Every time the return air temperature increases by 1°C, the exhaust temperature will increase by 1 to 1.3°C.
5. For the return air cooling compressor, the refrigerant vapor is heated by the motor when it flows through the motor cavity, and the cylinder suction temperature is once again increased. The amount of heat generated by the motor is affected by power and efficiency, while the power consumption is closely related to displacement, volumetric efficiency, working conditions, friction resistance, etc.
6. Although reducing the evaporation temperature can increase the freezing temperature difference, the refrigeration capacity of the compressor is reduced, so the freezing speed is not necessarily fast. What's more, the lower the evaporation temperature, the lower the refrigeration coefficient, but the load increases, the operating time is prolonged, and the power consumption will increase. To
7. Reducing the resistance of the return air pipeline can also increase the return air pressure. The specific methods include timely replacement of the dirty return air filter, and minimize the length of the evaporation tube and the return air pipeline. To
8. In addition, insufficient refrigerant is also a factor of low return pressure.
5. the temperature is too high
1. The refrigerant charge in the system is insufficient, even if the expansion valve is opened to the maximum, the liquid supply will not change, so that the refrigerant vapor in the evaporator will overheat and the suction temperature will increase.
2. The opening of the expansion valve is too small, resulting in insufficient refrigerant circulation in the system, less refrigerant entering the evaporator, high overheating, and high suction temperature. To
3. The expansion valve port filter is blocked, the liquid supply in the evaporator is insufficient, the amount of refrigerant liquid is reduced, and a part of the evaporator is occupied by superheated steam, so the suction temperature rises. To
4. The suction temperature is too high due to other reasons, such as poor heat insulation of the return air pipe or too long pipe, which can cause the suction temperature to be too high. Under normal circumstances, the compressor cylinder head should be half cold and half hot.
6. he temperature is too low
1. Too much refrigerant charge, occupying part of the condenser volume and increasing the condensing pressure, and the liquid entering the evaporator increases accordingly. The liquid in the evaporator cannot be completely vaporized, so that the gas sucked by the compressor contains liquid droplets. In this way, the temperature of the return air duct drops, but the evaporation temperature does not change because the pressure does not drop, and the degree of superheat decreases. Even if the expansion valve is closed, there is no significant improvement. To
2. The opening of the expansion valve is too large. The temperature sensing element is too loosely bound, the contact area with the air return pipe is small, or the temperature sensing element is not wrapped with insulation material and its wrapping position is wrong, etc., resulting in inaccurate temperature measurement of the temperature sensing element, close to the ambient temperature, causing the expansion valve to operate The opening degree increases, resulting in excessive liquid supply. To
7. The influence of evaporating temperature on refrigeration efficiency
1. The heating temperature has a great influence on the refrigeration efficiency. When it decreases by 1 degree, the same cooling capacity needs to increase the power by 4%. Therefore, if conditions permit, appropriately increasing the evaporating temperature is beneficial to improving the cooling efficiency of the air conditioner. of. The evaporating temperature of household air conditioners is generally 5 to 10 degrees lower than the air outlet temperature of the air conditioner. During normal operation, the evaporating temperature is 5 to 12 degrees, and the outlet temperature is 10 to 20 degrees.
8. exhaust temperature / exhaust pressure / exhaust volume
1. The main reasons for the high exhaust temperature are as follows: high return air temperature, large heating capacity of the motor, high compression ratio, high condensation pressure, adiabatic index of the refrigerant, and improper refrigerant selection.
2. For R22 compressor, when the evaporating temperature decreases from -5°C to -40°C, the COP will generally decrease by 4 times, and other parameters will not change much, and the temperature rise of the gas in the motor cavity will increase by three or four times. As the cylinder suction temperature increases by 1°C, the exhaust temperature can increase by 1 to 1.3°C. Therefore, when the evaporation temperature is reduced from -5°C to -40°C, the exhaust steam temperature will rise by about 30-40°C. In the return air cooling type semi-hermetic compressor, the temperature rise of the refrigerant in the motor cavity is roughly between 15 and 45°C.
3. In the air-cooled (air-cooled) compressor, the refrigeration system does not pass through the windings, so there is no motor heating problem.
4. The exhaust temperature is greatly affected by the compression ratio (condensing pressure/evaporating pressure, generally 4). Under normal circumstances, the discharge pressure of the compressor is very close to the condensing pressure. When the condensing pressure increases, the compressor discharge temperature also increases. The larger the compression ratio, the higher the exhaust temperature and the reduction of the air delivery coefficient, which reduces the cooling capacity of the compressor and increases the power consumption.
5. Reducing the compression ratio can significantly reduce the exhaust temperature. Specific methods include increasing the suction pressure and reducing the exhaust pressure. The suction pressure is determined by the evaporation pressure and the resistance of the suction line. Increasing the evaporation temperature can effectively increase the suction pressure and rapidly reduce the compression ratio, thereby reducing the exhaust temperature. To
6. Practice shows that reducing the exhaust temperature by increasing the suction pressure is simpler and more effective than other methods.
7. The main reason for excessive exhaust pressure is that the condensing pressure is too high (there is air in the system; the refrigerant charge is too much, and the liquid occupies the effective condensing area; the condenser has insufficient heat dissipation area, fouling, cooling air volume or insufficient water volume , Cooling water or air temperature is too high, etc.). It is very important to choose a suitable condensing area and maintain sufficient cooling medium flow.
8. Exhaust pressure is too low. Although the phenomenon is manifested in the high-pressure side, the reason is mostly at the low-pressure side.
9. Insufficient air displacement is mainly due to the fact that the compressor suction pipe is too long and the pipe diameter is too small compared with the compressor’s design air volume, which increases the suction resistance, affects the suction volume and reduces the discharge volume. .
9. liquid strike
1. In order to ensure the safe operation of the compressor and prevent liquid hammer, it is required that the suction temperature be higher than the evaporation temperature, that is, it should have a certain degree of superheat. The degree of superheat can be achieved by adjusting the opening degree of the expansion valve. To
2. Avoid excessively high or low temperature. If the suction temperature is too high, that is, the overheating is too high, which will cause the compressor discharge temperature to rise. If the suction temperature is too low, it means that the refrigerant is not completely evaporated in the evaporator, which not only reduces the heat exchange efficiency of the evaporator, but the suction of wet steam will also cause compressor liquid hammer. The suction temperature should be 5-10℃ higher than the evaporation temperature under normal circumstances. To
10. overheating
1. For the commonly used R22 refrigerant, the cooling capacity of the compressor decreases with the increase of the effective superheat. When the superheat is 10℃, the cooling capacity is 99.5% of the cooling capacity under saturated evaporation, and when the superheat is 20 At ℃, the cooling capacity is 99.3% of the cooling capacity under saturated evaporation. It can be seen that the attenuation of the cooling capacity with the increase of superheat is very small.
2. The refrigerant maintains a certain degree of superheat, which can further prevent the liquid hammer phenomenon in the cylinder. For low-temperature refrigeration systems, appropriately increasing the effective superheat can make the lubricating oil return to the compressor smoothly. But as the compressor suction superheat increases, its discharge temperature also rises. Excessive discharge temperature will make the lubricating oil viscosity thinner and even carbonize, affecting the normal operation of the compressor, so the suction superheat should be controlled Within a certain range.
11. Add fluoride
1. When the amount of fluorine is small or its regulating pressure is low (or partially blocked), the valve cover (bellows) of the expansion valve and even the liquid inlet will be frosted; when the amount of fluorine is too small or there is basically no fluorine, the appearance of the expansion valve No response, only a faint sound of airflow can be heard.
2. See from which end the icing starts, whether it is from the dispensing head or the return pipe from the compressor. If the dispensing head is short of fluorine, the compressor is more fluorine. -
 Causes and solutions for common failures of cold storage systems 2020-12-23
Causes and solutions for common failures of cold storage systems 2020-12-23Causes and solutions for common failures of cold storage systems
1.The suction temperature is too high
The suction temperature is too high-mainly caused by the increase in the degree of superheat of the suction. Note that the high suction temperature does not mean that the suction pressure is high, because the suction is superheated steam. Under normal circumstances, the compressor cylinder head should be half cold and half hot. If the suction temperature is too high, all the cylinder head will heat up. If the suction temperature is higher than the normal value, the exhaust temperature will rise accordingly.
The main reasons for the excessively high suction temperature are:
(1) Insufficient refrigerant charge in the system. Even if the expansion valve is opened to the maximum, there will be no change in the liquid supply, so that the refrigerant vapor in the evaporator overheats and the suction temperature rises.
(2) The opening of the expansion valve is too small. As a result, the circulation of refrigerant in the system is insufficient, the amount of refrigerant entering the evaporator is small, the degree of superheat is large, and the suction temperature is high.
(3) The filter screen of the expansion valve port is blocked. The supply of liquid in the evaporator is insufficient, the amount of refrigerant liquid is reduced, and a part of the evaporator is occupied by superheated steam, so the suction temperature increases.
(4) The suction temperature is too high due to other reasons. If the return air pipe is not well insulated or the pipe is too long, it can cause excessively high suction temperature.
2.The temperature is too low
The suction temperature is too low-mainly caused by the large liquid supply of the evaporator and the low suction superheat. (1) The refrigerant charge is too much. Occupies part of the volume in the condenser to increase the condensing pressure, and the liquid entering the evaporator increases accordingly. The liquid in the evaporator cannot be completely vaporized, so that the gas sucked by the compressor contains liquid droplets. In this way, the temperature of the return air duct drops, but the evaporation temperature does not change because the pressure does not drop, and the degree of superheat decreases. Even if the expansion valve is closed, there is no significant improvement.
The opening of the expansion valve is too large. The temperature sensing element is too loosely bound, the contact area with the air return pipe is small, or the temperature sensing element is not wrapped with insulation material and its wrapping position is wrong, etc., resulting in inaccurate temperature measurement of the temperature sensing element, close to the ambient temperature, causing the expansion valve to operate The opening degree increases, resulting in excessive liquid supply.
Reasons for the frosting of the compressor: Reason 1: As above Reason 2: The refrigerant charge is insufficient, and it will condense from the evaporator to the compressor; Reason 3: Due to external reasons, the refrigerant will not evaporate in the evaporator or even not evaporate. Severe frost, and even wet compression.
3.The exhaust temperature is abnormal Abnormal
discharge temperature-influencing factors: adiabatic index, compression ratio, suction temperature, and compressor discharge temperature can be read from the thermometer on the discharge pipe. It is related to the refrigerant's adiabatic index, compression ratio (condensing pressure/evaporating pressure) and suction temperature. The higher the suction temperature and the higher the compression ratio, the higher the exhaust temperature, and vice versa. When the suction pressure does not change, when the exhaust pressure increases, the exhaust temperature rises; if the exhaust pressure does not change, when the suction pressure drops, the exhaust temperature also rises. Both of these cases are caused by the increase in compression ratio. Too high condensation temperature and exhaust temperature are unfavorable to the operation of the compressor and should be prevented. Excessive exhaust temperature will cause the lubricating oil to become thinner or even carbonize and coke, thereby worsening the compressor lubrication conditions. The discharge temperature is proportional to the compression ratio (condensing pressure/evaporating pressure) and the suction temperature. If the superheat temperature of the suction is high and the compression ratio is large, the exhaust temperature is also high. If the suction pressure and temperature do not change, when the exhaust pressure increases, the exhaust temperature also increases. The main reasons for the increase in exhaust temperature are: (1) The suction temperature is higher. After the refrigerant vapor is compressed, the exhaust temperature is higher. (2) Condensing temperature rises. The condensing pressure is also high, causing the exhaust temperature to rise. (3) The exhaust valve plate is broken. The high-pressure steam is repeatedly compressed and the temperature rises, the cylinder and cylinder head are hot, and the indication value of the thermometer on the exhaust pipe also rises. The actual factors that affect the increase of exhaust temperature are: low intercooling efficiency, or excessive scale in the intercooler affects heat exchange, the suction temperature of the subsequent stage will inevitably be higher, and the exhaust temperature will also increase. The valve leaks and the piston ring leaks, which not only affects the increase in exhaust temperature, but also changes the pressure between stages. As long as the compression ratio is higher than the normal value, the exhaust temperature will rise. In addition, water-cooled machines, lack of water or insufficient water will increase the exhaust temperature. The condensing pressure is abnormal and the exhaust pressure is reduced.
4.Higher exhaust pressure
High discharge pressure-mainly caused by high condensing pressure, not the compressor itself. Exhaust pressure generally corresponds to the condensation temperature. Under normal circumstances, the discharge pressure of the compressor is very close to the condensing pressure. When the condensing pressure increases, the compressor discharge temperature also increases. The compression ratio of the compressor increases, and the air delivery coefficient decreases, so that the cooling capacity of the compressor decreases. Increased power consumption. If the exhaust temperature is too high, it will increase the consumption of compressor lubricating oil, make the oil thinner, and affect lubrication; when the exhaust temperature is close to the compressor oil flash point, part of the lubricating oil will also be carbonized and accumulated in the suction, The exhaust valve port affects the sealing performance of the valve. Reducing the temperature of the cooling medium can reduce the condensation temperature and the condensation pressure. However, this is limited by environmental conditions and is difficult to choose artificially. Increasing the flow of the cooling medium can lower the condensation temperature a little (this method is often used). However, the flow of cooling water or air cannot be increased one-sidedly, because this will increase the power of the cooling water pump or fan and motor, which should be considered comprehensively. Higher exhaust pressure will increase the compression work and reduce the gas transmission coefficient, thus reducing the refrigeration efficiency. The main reasons for this failure are: (1) the cooling water (or air) flow is small and the temperature is high; (2) there is air in the system, which increases the condensing pressure; (3) the refrigerant charge is too much and the liquid is occupied The effective condensing area is improved; (4) The condenser is out of repair for a long time, and the heat transfer surface is seriously dirty, which can also cause the condensing pressure to rise. The presence of scale also has a greater impact on the condensation pressure.
5.Exhaust pressure is too low
Exhaust pressure is too low-mainly caused by the low refrigerant flow in the refrigeration system pipeline or even stoppage. Exhaust pressure is too low, although its phenomenon is manifested in the high-pressure side, but the reason is mostly at the low-pressure side. The reason: the expansion valve is blocked by ice or dirty, and the filter is blocked, which will inevitably reduce the suction and exhaust pressure. -
Symptomanalysis of common failures in refrigeration system 2020-11-20
Symptomanalysis of common failures in refrigeration system
When a failure occurs in a refrigeration system, it is generally impossible to see directly where the failure site occurs, nor is it possible to dissect and dissect the parts of the refrigeration system one by one. Only by looking at the surface can abnormal phenomena be found in operation, for a comprehensive analysis. In the inspection generally through the look, listen, touch to understand the running state of the system. When the operating pressure and temperature of the system exceed the normal range, except indoor and outdoor environment temperature deterioration, otherwise there will be problems, which is an important basis for judging the source of failure.
1. Measurement of pressure and temperature of refrigeration system
(1) pressure concept of refrigeration system: The refrigeration system can be divided into two parts: high pressure and low pressure. The high pressure section from the compressor outlet to the throttle front, this section is called the evaporation pressure. The suction pressure of the compressor is called suction pressure, suction pressure is close to the evaporation pressure, the difference is the flow resistance of the pipeline.
For convenience, the evaporating pressure and condensing pressure of the refrigeration system are detected at the suction and exhaust ports of the compressor. That is often called the compressor suction, exhaust pressure. The purpose of measuring the suction and exhaust pressure of refrigeration system is to obtain the evaporating temperature and condensing temperature of refrigeration system, so as to obtain the running status of refrigeration system.
(2) the concept of temperature in refrigeration system: the temperature in refrigeration system involves a wide range, including evaporation temperature te, suction temperature ts, condensation temperature, exhaust temperature, etc. . The evaporating temperature te and condensing temperature TC are the decisive factors to the operating condition of the refrigeration system.
A. Evaporation temperature te: refers to the liquid refrigerant in the evaporator boiling vaporization temperature.
B. Condensing temperature TC: is the temperature at which the superheated vapor of a refrigerant condenses into a liquid after exothermic action in the condenser. The condensation temperature can not be measured directly either, only by detecting the corresponding condensation pressure, and then by consulting the thermodynamic properties of the refrigerant table. The higher the condensing temperature is, the higher the condensing pressure is. The condensing temperature is too high, the load of the unit is too heavy, the motor is over-loaded, and the operation is unfavorable.
C. Exhaust temperature td: refers to the temperature of the compressor exhaust port (including the temperature of the exhaust port nozzle) , testing exhaust temperature must have a temperature measuring device, general minicomputer is not set up, temporary measurement can be used semiconductor point thermometer detection, but the error is larger. The exhaust temperature is affected by the suction temperature and the condensation temperature, the suction temperature or the condensation temperature rise, the exhaust temperature rise accordingly, so it is necessary to control the suction temperature and the condensation temperature to stabilize the exhaust temperature.
D. Inspiratory temperature ts: refers to the gas temperature of the connecting pipe of the compressor suction, the temperature measurement device is needed to detect the suction temperature, generally, the suction temperature of air conditioning unit should be controlled around TS = 15 °C. Above this value has certain influence to the refrigeration effect.
2. Influence of suction pressure variation on refrigeration system
The suction pressure of a refrigeration system is closely related to the evaporation temperature and the flux of the refrigerant. For Systems using expansion valves, suction pressure is related to the opening of expansion valves, refrigerant charge, compressor cooling efficiency, and load. In a capillary system, suction pressure is related to condensing pressure, refrigerating capacity, compressor refrigerating efficiency, and load. Therefore, when inspecting the refrigeration system, the pressure gauge should be installed on the suction pipe. It is very important to detect suction pressure for fault analysis.
(1) factors of low suction pressure: The suction pressure is lower than the normal value. The factors include insufficient refrigeration capacity, small cooling load, small expansion valve opening, low condensing pressure (refers to the capillary system) , and unblocked filter.
(2) factors of high suction pressure: The suction pressure is higher than the normal value, such as too much refrigerant, large refrigeration load, expansion valve opening, high condensing pressure (capillary system) and low efficiency of compressor, etc. .
3. The influence of exhaust (condensation) pressure change on refrigeration system
When the refrigeration system is running, the exhaust pressure corresponds to the condensing temperature, and the condensing temperature is related to the flow rate of the cooling medium, temperature, refrigerant inflow, cooling load and so on. When the refrigeration system is inspected, an exhaust pressure gauge should be installed at the exhaust pipe to detect the exhaust pressure as the data for analysis of faults.
(1) factors of high exhaust pressure: When the exhaust pressure is higher than the normal value, the flow rate of the cooling medium is small or the temperature of the cooling medium is high, the refrigerant charge is excessive, the cooling load is large and the expansion opening is large, etc. .
The above factors will cause the increase of circulating flow and the condensation heat load. As the heat can not be all out in time, causing condensation temperature rise, and can be detected is the exhaust (condensation) pressure rise. When the flow rate of the cooling medium is low or the temperature of the cooling medium is high, the cooling efficiency of the condenser decreases and the condensing temperature increases. When the flow rate of the cooling medium is low or the temperature of the cooling medium is high, the cooling efficiency of the condenser decreases and the condensing temperature increases. The reason of excessive refrigerant charge is that the surplus refrigerant liquid occupies part of the condenser tube, which reduces the condensing area and causes the condensing temperature to rise.
(2) factors of low exhaust pressure: The exhaust pressure is lower than the normal value. The factors include low efficiency of the compressor, insufficient refrigerating dose, Small Cooling Load, small expansion valve opening, and unblocked filter, including expansion valve filter screen and cooling medium temperature low.
Above several kinds of factors all can cause the system the refrigeration flow to drop, the condensation load is small, causes the condensation temperature to drop.
From the above suction pressure and exhaust pressure and exhaust pressure changes, there is a close relationship between the two. In general, when the suction pressure rises, the exhaust pressure rises, and when the suction pressure drops, the exhaust pressure drops. Also may estimate from the suction pressure gauge change the exhaust pressure approximate situation.
4. The relationship between suction temperature and exhaust temperature
In fact, the exhaust temperature of the system is closely related to the suction temperature. Inspiratory temperature rises, exhaust temperature also rises relatively, otherwise is low. By understanding their relationship, you can control them and make the refrigeration system work better.
5. Effect of temperature change on refrigeration system of condensing unit
Unit components have normal temperature range, beyond this range is not normal state. These abnormal factors may be the fault, may be adjusted incorrectly, but it is necessary to analyze the cause, and timely processing or inspection. These temperature points are difficult to measure with a thermometer, generally can only be estimated by hand, and then judge whether normal.
(1) exhaust temperature effect: In summer, the exhaust temperature of the compressor is relatively high, hands can not touch. According to national standards, R22 refrigeration system exhaust temperature should not exceed 150OC, more than this temperature line is abnormal. The cause of super high exhaust temperature is due to super high suction temperature of compressor or super high condensing temperature, which must be noticed. Exhaust temperature is too low, hand-touch exhaust pipe is not hot, which means that the suction temperature is particularly low, compressor may run wet stroke or system working fluid is relatively small operating state. The compressor wet stroke is easy to damage the valve structure, the refrigerant is very few circumstances operation, will affect the motor winding heat dissipation, accelerate the aging of insulation material.
(2) the influence of casing temperature change on compressor and refrigeration system: The temperature field on the casing surface of a fully enclosed reciprocating piston compressor can be divided into two parts: A. The upper casing is affected by the inhalation of steam, the temperature is relatively low, in a slightly hot or cool range, it is estimated at about 30 °C, in the vicinity of the suction pipe local casing surface dew. B. The heat generated by the motor in the lower casing and the friction heat brought out by the frozen oil are mainly brought out of the casing by steam.
A. The influence and reason of too high temperature of Chassis: the surface temperature of chassis exceeds the normal range, mainly because the suction temperature of refrigeration system is too high (higher than 15 °c) . Too high hot steam into the compressor, absorbing heat in the casing, so that the steam temperature is higher, so that the temperature of the casing rise. Superheated steam temperature rise is very high, chassis temperature rise is very high, to the oil cooling, this will affect the lubrication of moving parts, accelerate wear, serious so that the bearing holding shaft (Bite) . In addition, it will cause the exhaust temperature to rise.
B. Chassis temperature is too low and the reasons: Chassis surface temperature below the normal range, the reason is too low suction temperature (less than 15 °C) . It is beneficial to the cooling of the oil and the motor windings, but the cooling capacity is decreased. When the inspiratory temperature is particularly low, will make most of the shell dew, there is the danger of hydraulic blow, this is the fatal blow to the compressor, should pay special attention. At the same time, a large amount of refrigerant is dissolved in the frozen oil, which is disadvantageous to the lubrication of moving parts.
(3) temperature condition of condenser
A. Condenser temperature status: normally, the first half of the heat pipe is very hot, and its temperature has a slow gradual decline in the balance. Compared with the front part, the heat-sensing degree of the latter part of the heat sink pipe is greatly reduced, which is due to the fact that the refrigerant in the latter part of the pipe has been liquefied gradually and has reached the condensing temperature and the supercooling temperature. When abnormal conditions occur, one is the front half is not too hot, the latter half near normal temperature (ambient temperature) , the reason is compressor hygroscopic steam refrigerant or refrigerant dose is insufficient. The other is the whole condenser tube is very hot, its reason is too much refrigerant or small ventilation, or high ambient temperature.
B. WATER-COOLED CONDENSER: the Shell of a shell-and-tube condenser is normally relatively hot in the upper half and lukewarm in the lower half. The abnormal condition is that the whole Shell is not too hot, the reason is not enough refrigerant. Another situation is that the whole Shell is very hot, which is due to insufficient cooling water or poor cooling effect (scaling in the pipe) . Casing condenser in normal circumstances, casing surface is very hot, its reason is too small cooling water or poor cooling effect; the other is the whole casing surface is not too hot, its reason is insufficient refrigerant. (4) temperature profile of the reservoir: under normal conditions, the suction tube feels cool to the touch of the hand and is covered with dew. The reason is the condenser cooling difference, high condensation temperature or refrigerant charge too much.
(5) the liquid tube temperature condition: under normal circumstances, the liquid tube is warm. Under abnormal circumstances, the liquid tube is relatively hot. The reason is the condenser cooling difference, high condensation temperature or refrigerant flow too much.
(6) filter temperature condition: The basic condition is the same as the infusion tube, but it has a prominent abnormal phenomenon, that is, the filter may be cool, the reason is that the filter hole is blocked by sludge, making the filter blocked, when the refrigerant flows through the filter screen, throttling occurs, that is, a part of the liquid gasification endothermic, so that the filter cool, serious condensation. Another abnormal phenomenon is the filter is not hot, and the ambient temperature, the reason is completely blocked filter, refrigerant can not flow.
(7) the temperature of the suction tube, under normal circumstances, the suction tube feel very cold by hand, and with dew. Abnormal circumstances, one is the inhalation tube cold, Dew too much, resulting in large-scale Shell dew. The reason is that the refrigerant flow is too large, the liquid can not be vaporized in the evaporator, there are liquid reflux phenomenon. Its harmfulness is the compressor may run wet stroke, serious will produce hydraulic blow, the valve plate is threatened. Second, the suction tube is not cold, not dew, the Shell is very hot. The reason is that the refrigerant flow is too small or the amount of refrigerant is insufficient. The result is an increase in exhaust temperature and a decrease in cooling capacity. -
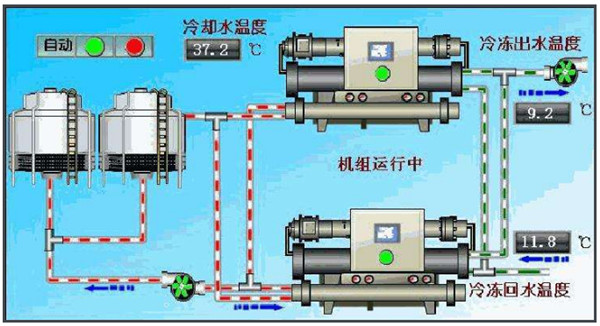 How to choose air conditioning main engine? What does common air conditioning main engine have? 2020-11-03
How to choose air conditioning main engine? What does common air conditioning main engine have? 2020-11-03How to choose air conditioning main engine? What does common air conditioning main engine have?
一、WATER-COOLED CHILLERS:
The water cooled chiller is part of the chiller in the air conditioning, and its refrigerant is water, called the Chiller, and the condenser is cooled by heat exchange of normal temperature water. So called water-cooled units, and water-cooled units known as the opposite of air-cooled units, air-cooled units by the condenser and outdoor air forced ventilation heat exchange to achieve refrigeration since.
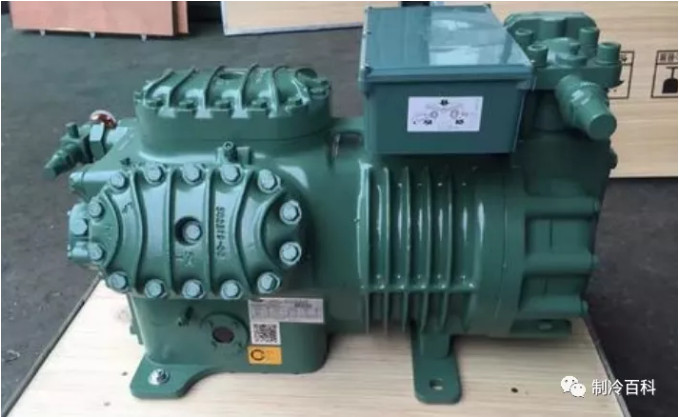
1、Screw chillers: Screw chillers are large and medium-sized chillers that provide chilled water. Commonly used in National Defense Research, energy development, transportation, hotels, restaurants, light industry, textile and other departments of air conditioning, as well as water conservancy and power engineering frozen. The screw type chiller is a complete refrigeration system which is composed of screw refrigeration compression group, condenser, evaporator, automatic control element and instrument. It has the advantages of compact structure, small volume, light weight, small area, convenient operation and maintenance, smooth operation and so on, so it has been widely used.
2、Centrifugal chillers: chillers are made up of Centrifugal chillers, complete with evaporators, condensers and throttling controls, and electrical meters. The capacity of a single chiller ranges from 700 to 420OKW. Applicable to sub-large and extra-large projects.
二、AIR-COOLED CHILLERS:
water-cooled chillers and air-cooled chillers, the main difference between them lies in the condenser. The condenser of a water-cooled chiller takes away heat mainly by circulating cooling water. Unlike water-cooled chillers, air-cooled chillers use fans for cooling. Finned condenser is usually used. The finned condenser is actually a piece of aluminum. The area where the heat transfer is about to take place is externally mounted with the finned condenser for efficient heat dissipation. The hot air is then discharged through a powerful fan.
The modular machine was developed on the basis of the VRV system, which was invented and patented in 1985 by the Czech Wind Group of Australia. It will change the traditional Freon pipeline into the water system, the combination of indoor and outdoor units into refrigeration units, indoor units into fan coil. The refrigeration process is realized by the heat transfer of the refrigerant water. The module machine is named because it can automatically adjust the number of starting machine according to the requirement of cooling load and realize flexible combination.
AIR-COOLED WATER SCREW MACHINE:
The difference between air-cooled screw and water-cooled screw is that a condenser adopts a fin-type condenser, another is a tube-shell type condenser, which is suitable for a large cold capacity factory, market.
三、VRV systemVRV system is the abbreviation of variable Refrigerant Volume system, I. E. Variable Refrigerant flow system. Its form is a group of outdoor machine, by the function machine and constant speed machine, frequency conversion machine composition. Through the parallel outdoor machine system, the refrigerating pipe is centralized into a pipe system, and the suitable capacity of the indoor machine is selected from 122.5 kw to 1.5 kw according to the matching of the capacity of the indoor machine, that is up to a group of outdoor units can be connected to 30 indoor units.
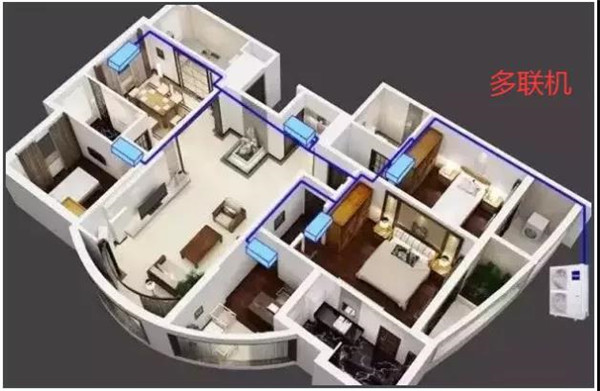
Indoor machine has ceiling embedded type, hanging wall type and so on. Different types of indoor single machine can be connected to a refrigeration loop, and can be controlled separately. The minimum capacity of indoor single machine is 0.6 kw and the maximum is 3.75 kw. The capacity of indoor machine can be adjusted from 50% to 130% of outdoor machine capacity.
四、How to choose a refrigeration unit
Calculate air conditioning cooling load according to the air conditioning area and room function of the building;
Statistical Building Air conditioning total load;
Most buildings need to consider the simultaneous use of rooms, the general simultaneous use of buildings for 70-80% , special circumstances need to be determined according to the building function and use;
The cooling load of the refrigerator is the product of the total air-conditioning load of the building and the simultaneous utilization ratio. According to the calculated cooling load of the refrigerator, both the refrigeration host can be selected;
The number of refrigeration units can be determined according to the building owner and the equipment room provided
The type of host machine can be determined according to the actual situation of the owner or according to the project situation, and the most suitable type of host machine can be chosen.
An office Gross leasable area for 2000 square meters, air-conditioning area for 1500 square meters, the whole building to use VRV system, should choose how much cooling capacity of the external unit?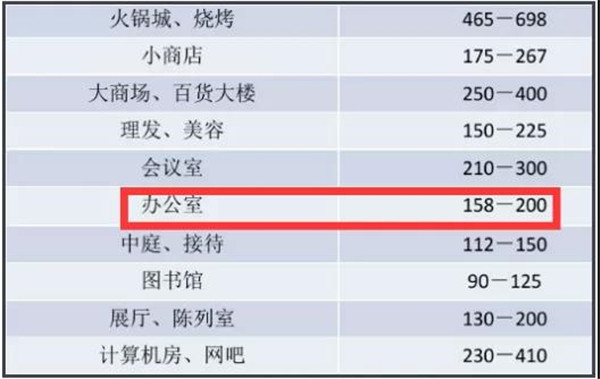
Calculations based on Empirical Cooling Capacity: 1500 m2200w/m2 = 300kw/2500w = 120hp.


